Today, the global online banking market size is projected to reach $31.81 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.6% from 2020 to 2027. The delivery of financial services is being more and more adjusted to web and mobile applications. Banking software is considered to be one of the most important with regard to its functionality, performance, user experience, usability, and security.
Hence, every banking application has to be flawless for end-users as it processes tons of confidential financial data. To ensure the app is seamless and works smoothly, there is a need for thorough online banking application testing. Thus, what is banking domain application testing? What test cases for banking application in software testing are applicable and highly important for BFS?
- This is What You Need to do Before Banking Application Testing
- Banking application's characteristics
- Banking Application Testing Checklist: All Test Cases and Requirements
- Mobile banking application testing requirements
- What bank application testing must include?
- Banking Application Security Testing: Regulations and Standards
- Performance Testing of Banking Application
- Bank Application Testing Stages: Our Workflow Step-by-Step
- Test planning
- Test design
- Test execution and evaluation
- Defect management
- Challenges in Banking Application Testing
- Security and Compliance
- Data Privacy
- Complex Business Logic
- Integration and Interoperability
- High Volume and Scalability
- Real-time Processing
- High Volume and Scalability
- Consider Inoxoft’s QA Automation Testing Services
This is What You Need to do Before Banking Application Testing
Banking software testing – is the process of finding defects in a software application and reporting these defects to the software engineers for further fixing. The more flaws quality assurance engineers can find, the more chances are that the final product will work smoothly. If the application you use has no bugs it means that the quality assurance team did their best job to enhance your user experience.
The process of testing is very important and is conducted in one of the software development lifecycle (SDLC) phases. Also, it is the most crucial stage. In the financial industry, banking app testing is an obligatory part of the process taking into account the data banks work with and the level of responsibility.
Banking application’s characteristics
The primary focus of testing a banking application is to understand what is the application like: is it a fully functional program? Or a supplement to an app? Or some other payment system/feature that has to be integrated into the banking application? Every banking app (or the integrated payment system) has its unique characteristics. Thus, it may include but is not limited to:
-
- Complex business workflows
- Multi-tier functionality to process numerous concurrent sessions
- Real-time processing
- High rate of transactions per second
- Batch processing
- Secure transactions
- Massive storage system
- Tracking and reporting section/a>
- Tracking and reporting section
- Recovery management
- Large-scale integration with multiple banking applications
Banking Application Testing Checklist: All Test Cases and Requirements
Having a complete understanding of the object to be tested, the quality assurance engineer figures out what are the requirements, and what types of testing to initiate. For instance, there is a general structure of mobile banking application testing. These may vary according to the company provider, the requirements of the client, and the very app to be tested. Be aware of all requires test cases for banking application in software testing:
Mobile banking application testing requirements
- Requirement Analysis. This stage is the primary and consists of requirements gathering and evaluations.
- Requirement Review. The stage presupposes a second look at the requirements of both sides (the client and the service provider) and their preparation to be documented.
- Business Requirements Documentation. This is the written document with all the quality assurance testing requirements that are to be adhered to within the whole process of testing. As this document is agreed upon by the two parties, its altering is impossible unless there is a solid reason.
What bank application testing must include?
- Database Testing. This is a layered process of testing. It has the user interface (UI) layer (interface design of the database), the business layer (database supporting business strategies), the data access layer, and the database itself.
- Integration Testing. This type of testing requires individual software modules to be combined and tested as a group. Thus, the testing aims at evaluating the compliance of a system or component with the app’s functional requirements.
- Functional Testing. The test cases of functional testing ground on the specifications of the software component under test. Functions are tested by making input and examining the output. The test cases of financial apps at Inoxoft are conducted with the help of fake cards. These cards (fake input) aim at understanding the quality, speed, and accuracy of payments (output) that are recorded in the banking app history, but no payments are deducted from the card.
- Security Testing. One of the most crucial digital banking app testings belongs to security compliance issues. Security flaws in the financial sector can cause damage to any stakeholder involved. What are the security protocols each banking app should adhere to?
Banking Application Security Testing: Regulations and Standards
- The General Data Protection Regulation (EU) 2016/679 (GDPR). This regulation functions in the EU and addresses the issue of personal data transfer outside the EU giving individuals control over their personal data and simplifying the regulatory environment for international business by unifying the regulation within the EU.
- The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC), according to which five banking regulators are “empowered to prescribe uniform principles, standards, and report forms to promote uniformity in the supervision of financial institutions.”
- ISO/IEC 27001, which provides requirements for any information security management system, e.g. the banking application. Using this regulation allows organizations to manage the security of financial information, intellectual property, employee details, or information entrusted by third parties.
- International Standard on Assurance Engagements 3402 (ISAE 3402). It is an international assurance standard that assures customers and service users of any organization that customers will receive adequate internal controls.
- The EU-U.S. and Swiss-U.S. Privacy Shield Frameworks provide companies with a standard to comply with data protection requirements when transferring personal data from the European Union and Switzerland to the United States.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, is designed to provide communications security over a computer network, especially in written and voice messaging. Client-server applications use this protocol to communicate across a network in a way designed to prevent eavesdropping and tampering.
Of course, these are only a part of the existing protocols mentioned but nonetheless important in banking app development and further banking domain testing. What concerns the banking app security testing phase, it includes testing of integrations with other apps, unsecured communications, security breaches that allow malware to be installed, utilization (and integration) of different authentication procedures, and testing hidden parts of the application.
- Usability Testing. It is a type of testing used to evaluate an application by testing it on users, giving direct input on how real tech-savvy users use the system.
- Acceptance Testing. A test case belonging to this type of testing determines if the requirements of a business requirements documentation are met. It involves performance testing.
Performance Testing of Banking Application
Performance testing of banking application is the process of checking the complete banking app (and not only banking) for possible flaws in the way it works by giving it a certain workload. Thus, the main focus of this banking domain application testing is to find out the speed, scalability, and stability of the system.
Hence the speed is measured to understand the velocity of app responses, and scalability measurement shows the maximum number of users that can use the application at once and it will not crash. And, stability shows whether the app works as a clock under different loads or if there are possible defects. Performance testing includes:
1. Load testing
3. Scalability testing
These testing types together with test cases for banking application in software testing aim at finding problems and flaws in an app. After extensive testing procedures, the following problems might be found:
- Poor time of response
- Poor scalability
- Bottlenecks (CPU-utilization, memory utilization, network utilization, operating system limitations, disk usage)
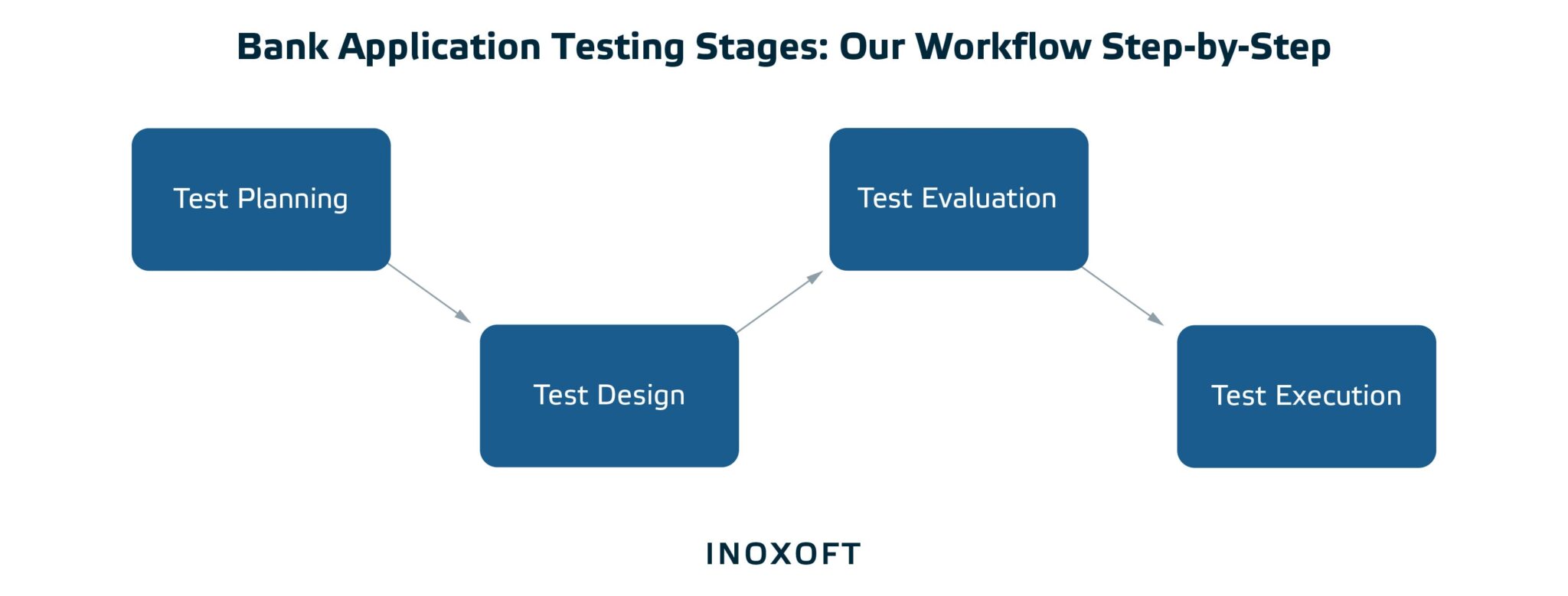
Bank Application Testing Stages: Our Workflow Step-by-Step
At Inoxoft, the workflow of the testing process looks as follows. It includes test planning, test design, test evaluation, and test execution.
Test planning
The stage of test planning includes developing test guidelines for a project with the input artifacts such as Test Guidelines (Organizational level) and Case Development, and the forecasted output artifact should be the revised Test Guidelines.
Also, the purpose of test planning is to set the focus of the test effort for each iteration together with stakeholders’ agreement on the defined goals that will drive the test effort. The input artifacts are Iteration Planning, Software Development Planning, Use-Case Model, Design Model, and Deployment Model. Based on the input, the output artifact should be a complete Test Plan.
Test design
The purpose of the test design stage is to figure out a set of verifiable Test Cases (for each build) and test procedures showcasing the realization of these Test Cases. The input artifacts should include Test Plan, Use Cases, Supplementary Specifications, Test Guideline, Iteration Plan, Software Architecture Document, and Design Guidelines. Thus the output artifacts are the complete Test Cases.
Test execution and evaluation
The purpose of test execution is to obtain test results. The results have to be verified and defects logged as necessary to be altered. So, the artifact input encompasses both Test Build and Test Scripts. The output artifact will be the Test Results.
Evaluating tests presupposes test result assessment, making log changes on requests, and calculation and delivery of key measures to produce the Test Evaluation Summary. Thus, the input artifacts are the Test Results and the output – Test Evaluation Summary and Test Log.
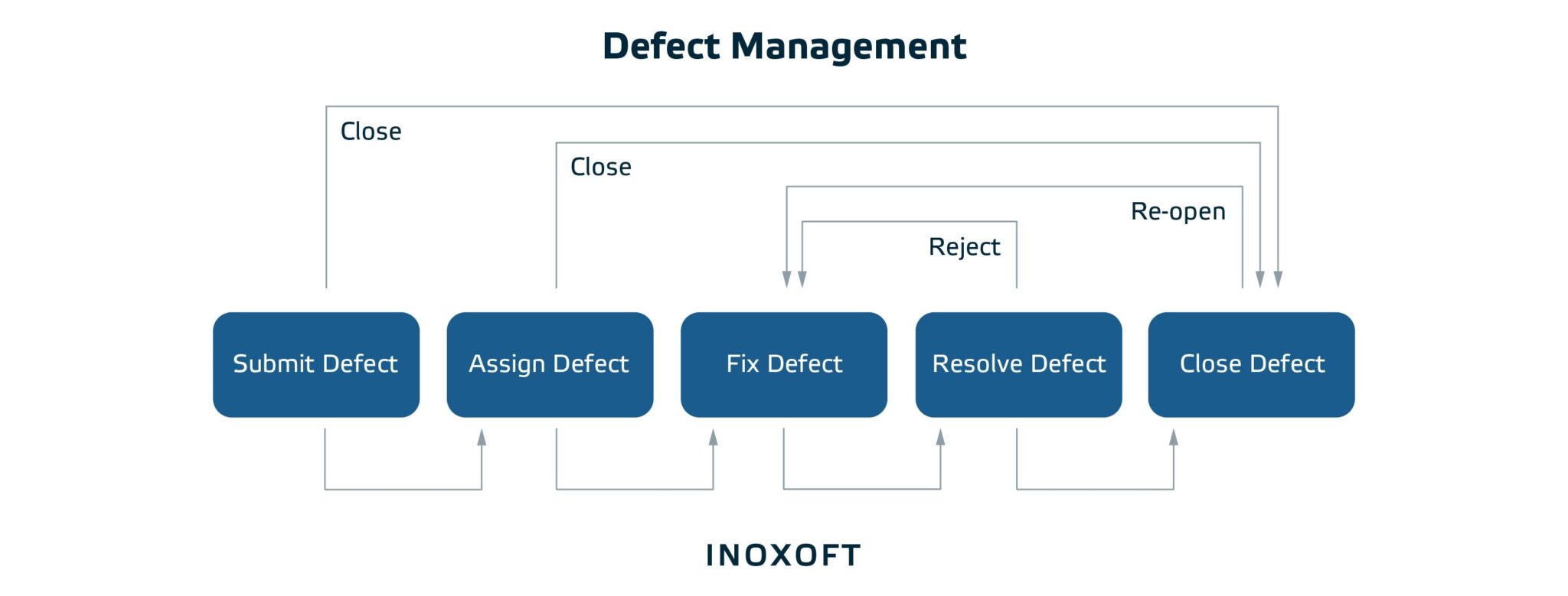
After these 4 stages, there is a possibility the software will include defects. Hence, there also is the fifth stage, where these defects are managed.
Defect management
The stage is designed to resolve and measure defects or incidents found in the software product. This way, these defects have to be identified and reported. So, the input artifact of Test Results should generate the Software Defect output artifact that is further submitted and fixed by software engineers.
Challenges in Banking Application Testing
Testing for banking applications can create some challenges due to their complex nature and the criticality of the systems involved. Here is a list of the key challenges in software testing for banking:
Security and Compliance
Banking applications deal with highly sensitive customer information and financial transactions. Ensuring the security and compliance of these applications is crucial but challenging. Meeting industry standards, such as PCI DSS, GDPR, and various regulatory requirements, adds complexity to testing efforts.
Data Privacy
Protecting customer data privacy is the most important in banking apps. It requires thorough testing to ensure that sensitive information is properly handled, stored, transmitted, and accessed with appropriate security measures.
Complex Business Logic
Banking applications have complex business rules and workflows. Banking web application testing intricates test scenario like loan calculations, interest accruals, account reconciliations, and transaction processing, which requires a deep understanding of the banking domain and meticulous test design.
Integration and Interoperability
Banking systems integrate with numerous internal and external systems, such as core banking systems, payment gateways, and third-party services. Ensuring seamless accurate data exchange between these systems can be challenging during testing.
High Volume and Scalability
Banking applications must handle a high volume of transactions. Testing the application’s performance, scalability, and load-handling capabilities is essential to ensure uninterrupted service and a positive user experience.
Real-time Processing
Banking applications are expected to provide real-time transaction processing (e.g. fund transfers and balance updates). Testing the application’s real-time capabilities, including response times, event handling, and transaction consistency, is crucial.
High Volume and Scalability
Banking applications must handle a high volume of transactions. Testing the application’s performance, scalability, and load-handling capabilities is essential to ensure uninterrupted service and a positive user experience.
Consider Inoxoft’s QA Automation Testing Services
Inoxoft provides web application and financial application testing services as it is an automation testing company. Mobile development is changeable and Inoxoft tries to follow all the trends and updates of software development and testing. Our team of QA experts offers to conduct accurate testing, monitoring, coding, and design solution controlling to ensure the best quality of your app.
Also, Inoxoft provides QA testing of different size web applications. To do this, we utilize test automation services with the latest tool upgrades at your service. We provide QA automation services to deliver applications that meet market challenges and are fast, user-friendly, and scalable. If you need fintech industry app testing and one of the best customer-oriented services or detailed answers to your QA-based questions – let’s talk!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is banking application testing?
Banking application testing evaluates the functionality, performance, security, and reliability of software applications used in the banking and financial industry. It includes a series of tests and validations to ensure that the banking application meets the required quality standards, regulatory compliance, and user expectations. Key objectives of banking application testing are :
- Functionality Testing
- Security Testing
- Performance Testing
- Compatibility Testing
- Usability Testing
- Regression Testing
- Integration Testing
- Compliance and Regulatory Testing
What stages are in banking domain application testing?
- Test planning
- Test design
- Test execution and evaluation
- Defect management
Read the full article to discover details.