Minimum viable product development may become your business’ safe boat. Especially, if you’re a startup. According to the statistics, 20% of new businesses fail after one year of competing in the market, and about 50% of startups fail after four years.
You’d probably ask yourself, what leads these new companies to unexpected losses? The answer is simple. The idea they’ve put at the core of their business was not researched enough and proved to be not feasible. And, eventually, this idea got low or no user demand on the market. Many more factors you haven’t even expected also added to product failure.
So, if you have a choice, start with building a Minimum Viable Product if there is a need:
- to show customers an app that works
- to make money out of the application
- of a bug-free app ready to be marketed
- of higher retention rate at a low cost
- to know the market feedback for an application to proceed
With the help of building an MVP for startups, you can ensure your idea is worth building as while making research, building a product, and measuring data, you get to learn ideas, their advantages, and disadvantages. That’s why you need to consider minimum viable product development before initiating full product development and getting nowhere with it
Why exactly is it a safe boat? Because it allows you to:
- gather early feedback from the end-users
- facilitate faster time-to-market
- save the product from failure
And, most importantly, it may save your time, money, and effort by pointing out your product’s strengths and weaknesses from the start.
This article explores the significance of MVP development, citing examples of renowned companies that started with successful MVPs like Airbnb, Amazon, Uber, and Facebook.
- What Do you Need to Know in Developing an MVP?
- MVP's purpose
- MVP standards
- The Most Popular and Successful MVP Projects
- Airbnb
- Amazon
- Uber
- Types of Minimum Viable Products
- Landing page MVP
- Single-feature MVP
- Wizard of Oz
- Concierge MVP
- Top 5 Reasons for Building an MVP for Startups
- Focus on your users
- Reduce money wastage
- Speed up the time-to-market
- Reduce all the related risks
- 5. Choose the best option there is
- How to Build a Minimum Viable Product in 6 Simple Steps?
- 1. Identify your business and market needs
- 2. Create a user journey
- 3. Map out what you need to solve and plan detailed solutions
- 4. Decide on the limited features you need to build
- 5. Build an MVP and test it
- 6. Receive feedback and analyze results
- 6 Development Mistakes to Avoid While Building an MVP
- Prioritizing "minimum" over "viable"
- Targeting the wrong user segment
- Neglecting the right team dynamics
- Overlooking user feedback
- Creating an excessively complex MVP
- Failing to manage user feedback
- MVP Implementation Drawbacks
- Balancing feature significance
- Scalability сoncerns
- Privacy and intellectual property
- Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
- Final Thoughts
What Do you Need to Know in Developing an MVP?
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a product with minimum built features to satisfy early customers and collect feedback for further development. Business MVP is a potential solution offered to the end-users that can check the viability of the core idea behind it. MVP development belongs to the Discovery Phase Services and allows verifying the app’s feasibility, the team’s assumptions about the application, its usability, and market demand. MVP is a limited version of the full product but has enough features and functionality to gather the end-user valuable feedback.
Features of MVP that make it an outstanding solution include:
- bigger development readiness
- continuous feedback with higher value possibility for users
- small investment with higher retention
- eliminated money and time-wasting
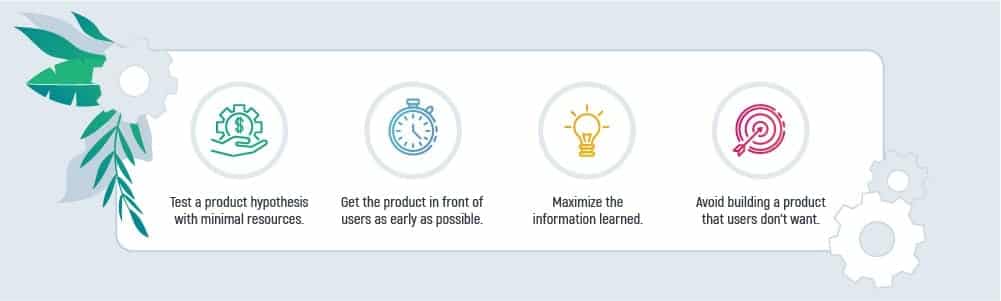
Having these features at its stake, MVP’s aim is to:
- test a product hypothesis having minimum resources
- show the product to users as early as possible
- enhance the information learned
- avoid product building if that is not what the users want
Learn how to test MVP to save your money and nerves!
If your choice falls on MVP development, the benefits you get will be extensive. Starting your product development with an MVP makes it possible to:
- get idea validation in the fastest, cheapest, and most efficient way
- experience easier changes in the process and less money/time will be consumed
- sell MVP as a ready-to-market product
- receive customer feedback faster
Steve Blank, an entrepreneur, who wrote numerous books about Startups, gives a piece of advice on how to create an MVP:
You’re selling the vision and delivering the minimum feature set to visionaries, not everyone.
MVP’s purpose
By commencing with a small-scale use case, a minimum viable product allows for essential idea validation and real-world testing. This process provides invaluable insights, which enables the efficient allocation of resources (in terms of time and cost), focusing on the core functionalities that deliver the most value.
In the B2B sphere, an MVP is considered viable when it’s marketable with the importance of commercial viability. It also acts as a risk mitigation strategy, identifying potential challenges and flaws early in the development process. This, in turn, aids in making informed decisions about whether to pivot the product in a new direction or to persevere with improvements.
MVP standards
Even though there is no strict set of universally defined standards for MVPs, there are some generally accepted principles and best practices for building MVPs.
A minimum viable product must offer genuine value to users while addressing a specific need or problem. Minimalism and testability are crucial, encompassing only essential features and the analytics mechanisms for robust data collection, since the initial version is serving as a foundation for ongoing improvements based on user feedback.
The Most Popular and Successful MVP Projects
Among the most popular and successful businesses that started their development and scaling from an MVP we can find:
Airbnb
It’s one of the most popular and user-favorite companies that allow easy, convenient, and cheap home rentals worldwide during vacations. This startup was founded in 2008 by Brian Chesky, who acknowledged the lack of places to stay for the night while traveling. Airbnb started offering short-term living apartments and breakfast for people, who found it hard or were short on money to book a hotel.
The startup grew due to getting commission out of every booking. The MVP project of Airbnb was a shallow website with 3x airbeds and breakfast. However, with constant customer feedback and meeting their short stay needs this MVP has grown into a fully-fledged product being available both on the web and on mobile gadgets. Last year the startup became a public company and raised $3.5 billion in revenue.
Amazon
This is an international technology company focusing on e-commerce, cloud computing, digital streaming, and artificial intelligence. It was founded in 1994 in a garage by Jeff Bezos. It was a startup that had a lot of time and effort input to make it work. According to Entrepreneur, Amazon became such a prosperous and huge company due to building a great MVP first. When Amazon launched, it was no more than an online bookstore. It was easy to start with books as people did not trust online shopping and ordered mostly books that were shipped to them immediately.
But, Bezos’s vision did not stop with books, he wanted to ship everything. So, starting simple was a great choice to gain some money and iterate on the MVP constantly enhancing its capabilities and breaking the boundaries. On gaining customer feedback and giving them what they wanted, the company grew outstandingly fast and offered society more available products, and even technological tools the software development sector finds extremely useful even today – the Amazon Web Services (AWS). In 2020, Amazon received $386.064 billion in revenue.
Uber
A company that specializes in services of ride-hailing, on-demand food and package delivery, courier availability, and freight transportation. It also allows renting electric bicycles and motor scooters. It was established as a startup in 2009 by Garett Camp. At that time technologies became important in human life and society was in search of convenient time-saving services that were also personalized and cheap. Uber started with an MVP release – a beta version, i.e. a simplified mobile interface used by a limited circle of people (founders and friends).
The access to the beta app was closed unless you emailed founders to open it. As the startup grew, the app gained more and more add-on features like live-tracking of drivers, fare splitting, automatic credit card payments, and fare estimates. At first, Uber had a small user base in San Francisco it provided services for. However, by focusing on user needs and improving services, it scaled pretty quickly and became international. Today, it is a top service provider with a user-friendly convenient app. In 2020, Uber’s revenue reached $11.139 billion.
An international online social media and social networking service (marketing) founded by Mark Zuckerberg in 2004. The initial aim of Facebook was to allow Harvard students to communicate with each other. The primary concept of Facebook was to show users two pictures of students and users had to make a choice of the hot student and the one not so hot. The social media app was closed to the rest of the world.
However, the users from the other universities entered to such an extent that the app became public and popular globally. The services it provided scaled as well. Facebook also started its growth from a simplified web MVP – a basic model of the product that had only the needed functionalities. The application was released to be tested and to gain valuable feedback. Nowadays, Facebook counts 2.85 billion monthly active users. And it doesn’t want to stop scaling.
Types of Minimum Viable Products
You often must dedicate a significant amount of time, sometimes stretching into thousands of hours, to develop a refined product that fulfills genuine user needs. Let’s examine some of the strategies to create a MVP that slashes development time while increasing the likelihood of making an impeccable product.
Landing page MVP
The most common way to develop a minimum viable product is to create a site, usually one-page, that showcases a brief description of product specificities, advantages, and CTAs to attract users to try out the product. In the shortest possible time, you will have your potential customers’ contacts collected but also achieve validated information about the product’s desirability.
Single-feature MVP
The approach, which Spotify and Foursquare used in their early stages, focuses on software products designed to test user acceptance of a specific core functionality. It’s a cost-effective way to enter the market and establish your product’s reputation. Benefits also include faster development and entry for small businesses. Despite lower user engagement and potential for complaints due to limited functionality, you can easily upgrade the product with other valuable features your audience prefers.
Wizard of Oz
In Wizard of Oz MVPs, you present the audience a finished product with an entirely developed interface from the front, while manually executing features behind the scenes. This cost-effective method allows you to estimate market interest before committing to actual development. With user validation, you can decide how to make the best-automated process for a flawless product usage experience.
Concierge MVP
Similar to the Wizard of Oz MVP, this approach makes a product mimic a multifunctional software solution with manual service for primary delivery. The difference is that concierge MVP users are aware of human assistance through the product’s use. Even though it relies heavily on human competency to maintain service quality, this approach is valuable for learning customer behavior, determining efficient automation methods, and genuine interest in your product.
Top 5 Reasons for Building an MVP for Startups
How to plan an MVP? An MVP template for startups is rather a need than an option to choose. Understanding all about building a minimum viable product, you will have the opportunity to:
Focus on your users
It is always vital to understand, who are you building your product for and what user problems it should resolve. For example, your idea of a startup is brilliant, but it hardly resolves any user issues. Thus, users won’t need it, won’t use it, or buy it. The biggest investors in your business growth are your users. So, find out what users want and need to have in their lives and give them what they demand. In addition, after you show them the MVP, you will receive feedback that might help your product evolve in the right direction.
Reduce money wastage
Unfortunately, startups emerge on the market being limited in their expenses. As they strive to find the gold mine, startups need to act carefully not to fail. And, developing an MVP is exactly the way to reduce costs. Making a simple product with minimal features and limited functionality will give users an idea of your app and will take fewer expenses. To test your idea on the market in such a way will be enough and not so damaging to the startup budget.
Speed up the time-to-market
For startups, it is a crucial goal. The faster you get your product to the end-users the faster you’ll get the audience interested, possible feedback to evolve, and revenue. What’s more, if you have competitors and they reach the market sooner, your startup might not get its potential customers. Thus, the time of your product development should be as short as possible.
Here, an MVP is a good choice to make a valuable product for a reasonable time and make consumers excited with your idea. Besides, if the time to develop a full product can be as long as years, then the tech MVP will take up to several months.
Reduce all the related risks
That’s when you have to view the statistics of how many % of startups fail. Of course, everyone wants their idea to succeed, but only the best well-thought startups win. With the help of an MVP, you get to reduce costs and achieve a faster-to-market functional product. In the same way, you relieve your startup of possible risks. Let’s speak about the two outputs you can get with an MVP:
- you lose, but invest little into the product and will have the opportunity to think it over to meet the consumer demand and try again
- your product wins and you’ll have extra budget to make an MVP into the fully functional application
Each road has its benefits, but your risk stays insignificant.
5. Choose the best option there is
There is only one alternative to building an MVP and it is fully-fledged product development. However, if you remembered the previous points, the MVP methodology has all the chances to reduce money and time wastage, decrease risks, and involve minimum efforts for the working end solution. The full product won’t give you these opportunities. You will have to trust your guts without testing the idea’s feasibility and saw what you will reap in the end.
Thus, think twice if you’re willing to put everything on fate or build your success with your own hands. Why should you engage in the full product development if you’re not sure your end-users will like it? Test the simplified version first.
How to Build a Minimum Viable Product in 6 Simple Steps?
How to make an MVP app? Building a full product requires Agile Methodology or any other method that the business use in its daily development processes. How to build an MVP? The same goes for MVP. As a part of the discovery, the MVP building process has main steps it covers. There are 6 steps to building an MVP. For example, creating a minimum viable product
1. Identify your business and market needs
To ensure your product is innovative and in-demand among users, answer the following questions dedicated to the MVP development process:
- Is there a need for your product or service in the market?
- Who are your competitors?
- What kind of product or service do you need to create to stand out?
In answering these questions target your startup’s long-term goals:
- What are you planning to achieve at the end?
- What will define the success of your product or service?
If you get to answer every question you will get the full picture, an MVP plan of your business needs, and market possibilities.
2. Create a user journey
How to create a minimum viable product? Look at your product or service from the user’s perspective. This way you will open up a new side to the MVP development that will show you how your potential user will use the product from opening up the application to making an order, a purchase, etc. So, the main process will look like this:
- User identification
- User actions identification
- User goals identification
By acknowledging users’ needs and priorities, you will design the MVP according to the user flow and propose an excellent solution that will be functional and comfortable to use. Your user is your biggest source of information and inspiration.
3. Map out what you need to solve and plan detailed solutions
To add value, you should make a table with the user pain points you have defined earlier and produce a solution for every point up to the benefits users will obtain using your solution. This way your MVP will focus on the most important areas as it cannot cover them all. In the process of MVP enhancement, you can add the least important features. But do start from the most crucial ones.
4. Decide on the limited features you need to build
Establish the right priority. Choose the potential product features that have high priority and leave the ones with the lower priority for further development. However, choose the most needed features not to compromise your user’s experience. Think about what your business goal is and try to adjust feature deployment to that goal. Then, add features gradually after each customer’s feedback.
Discover more: what are the limitations of progressive web apps?
5. Build an MVP and test it
This step requires the process of building an MVP and testing it. If you have a team to do the job – then everything’s in your hands. However, if you don’t, consider outsourcing one. There are four best countries to outsource your MVP development. Hire a dedicated team consisting of both software engineers and quality assurance testers and ensure your MVP will be a success.
6. Receive feedback and analyze results
After your MVP launch, collect user feedback. Find out what kind of feedback you should be measuring here. User behavior will tell you a lot about your product and set you on the right track towards further growth and product or service development. Don’t neglect this stage. Develop, test, learn and measure until you will be able to finalize the product or service.
Of course, this process may differ according to the company you choose to carry out this task.
Discover how to hire developers for a startup and how to run a successful startup!
6 Development Mistakes to Avoid While Building an MVP
When building a minimum viable product, keep an eye for several common development mistakes that you should avoid to increase the chances of success:
Prioritizing “minimum” over “viable”
Always bear in mind that the purpose of creating an MVP is to assess the viability of your product with as few features as necessary. Any product introduced to the market should still be technically sound, providing a user experience that encourages repeat usage.
Consider the most straightforward approach to gather the highest number of validated insights from users while ensuring a high-value experience. Avoid the pitfall of incorporating numerous mediocre features, when what you truly need are a couple of outstanding ones.
Targeting the wrong user segment
Attempting to solve every problem for a wide audience can lead to a diluted value proposition and a lack of relevance for individual users. Rather than that, design your product to address the specific needs of a particular user group — that’s how you’ll gather precise, high-quality feedback that is invaluable in shaping your product’s future direction.
Neglecting the right team dynamics
The team you assemble is the cornerstone of success; hence, hiring the wrong people to develop your MVP can prove detrimental to your venture. Besides looking for team members who have the necessary technical skills, make sure they share your vision, values, and commitment to the project.
The right team will bring a diverse range of perspectives, enhancing problem-solving and innovation throughout the development process. That’s why Inoxoft offers guidance in identifying and recruiting the right technical stakeholders, ensuring our clients’ projects are in capable hands from ideation to execution.
Overlooking user feedback
While it may seem like common sense, some might ignore the feedback and become overly fixated on the solution they envision rather than the problem they aim to address. Always remember the core purpose of creating a minimal viable product: to assess whether the expected solution effectively resolves the issue for your target audience. The only way to truly gauge the outcome of this test is by actively listening to those using your MVP.
Creating an excessively complex MVP
Over-complicating your MVP can have significant repercussions — dedicating a substantial portion of the budget and time to custom coding and manual architectural setup instead of utilizing frontend frameworks can result in a waste of time and resources.
Why generate a code that won’t be applicable in future product iterations and only serves to prolong the project? It doesn’t provide added value to the product and its end users and underscores the importance of striking a balance between innovation and practicality.
Failing to manage user feedback
When user numbers are limited, prioritizing specific features can be challenging: what some users consider crucial may not hold the same weight for others. Such an uncertainty carries the risk of allocating resources to features that may not be universally essential.
If you want to avoid iterative reworkings of the product, discern about the sources and the relevance of feedback during the MVP phase. Focus on incorporating suggestions that align best with your primary objectives and cater to your target audience’s needs.
MVP Implementation Drawbacks
Being aware of the potential challenges makes creating a minimum viable product easier. Let’s look at the not-so-obvious pitfalls and issues in MVP development:
Balancing feature significance
Deciding which features should be included in the initial MVP is a challenging task: too many features can lead to prolonged development and increased costs, while too few features may not effectively address the client’s needs. In the rush to create a lean and testable version, there’s a risk of inadvertently omitting features that are crucial for user adoption and satisfaction.
A lack of comprehensive market research or user feedback analysis can lead to a misjudgment of what constitutes a ‘core’ feature. Without a deep understanding of user pain points and needs, it’s dangerously easy to underestimate the importance of certain functionalities.
Scalability сoncerns
When teams focus primarily on delivering a minimum viable product, they may inadvertently neglect the underlying architecture’s ability to handle future expansions. This oversight can stem from a desire to swiftly enter the market and gather feedback, often taking precedence during the MVP phase.
The rush to create a minimum viable product can result in the selection of technologies and frameworks that expedite initial development yet not be equipped to support a more extensive user base or additional features down the line. As user numbers increase, the system may experience performance bottlenecks or failures, necessitating a comprehensive overhaul of the architecture.
Privacy and intellectual property
One notable challenge in the form of privacy concerns arises from the simplified nature of an MVP: to expedite market entry, creators often streamline features, inadvertently exposing potential vulnerabilities, which can inadvertently provide a more explicit blueprint for competitors to emulate.
The rapid development and testing process inherent to an MVP can inadvertently expose sensitive data, potentially putting it at risk. A lack of robust privacy measures during MVP development can leave businesses vulnerable to data breaches, which erode customer trust and potentially lead to legal consequences.
Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
Building an MVP is a creative and challenging process that requires great analytical skills, technology trends knowledge, and expertise in software development solutions that are meant for the end users. Therefore, by choosing Inoxoft your trusted software-building partner you will achieve:
- Solid market research of your idea by our team of experts
- Product feasibility proof and potential user analysis
- Defined scope of work with prioritized features that will also be documented
- Possibility to save costs and faster time-to-market
- A functional end-product that will work, be user-oriented, and meet the set goals
Also, you will receive recommendations on how to develop a minimum viable product, what will best suit your MVP, and a creative expert vision of our team that knows what users need and require these days.
Inoxoft is an international software development company that is among the best web development companies in new york. Our company offers to build top-notch MVP solutions and provide software development services for startups. Also, we are a UI/UX development company providing custom web development services all around the world. Hire our developers for your startup and receive the best quality solutions on the market. We have extensive experience and know how to develop an MVP and how to design an MVP (prototyping).
Inoxoft has 8+ years of experience in the international software development market. We have a complete understanding of what users want these days and how to make a minimum viable product. So far, Inoxoft has provided life-changing Discovery Phase Services for startups and other businesses that wanted to understand where they stand and what their advantages in launching a product will be. Here, the best solution we recommended and will always recommend is to build an MVP.
It is the best option for developing a functional product that will satisfy the basic user needs and give feasibility insights and almost immediately to allow the product to advance and scale. Our clients turn to us because we carry out our research, requirements analysis, and project management professionals, and are forward-thinking and goal-oriented. Your business success is also our success because we care.
Contact us, if you have an idea for a startup but hesitate whether it is feasible and the users need it. We will define MVP’s basic needs, help to meet goals by solving issues, and know-how to build an MVP that might be as successful as Airbnb, Uber, Facebook, or Amazon one day. Dream big and choose Inoxoft to implement your ideas!
Final Thoughts
To sum up, if you are a startup with an idea for a product launch in the technology market, don’t waste your time and choose to build an MVP. How to launch an MVP? This is the right way for you to prepare for the market, understand user needs, solve their pain points, reduce risks that occur due to insufficient analysis and knowledge and achieve a simplified version of the future full product. The benefits of choosing MVP development are extensive. You will shorten the development time and rescue time wastage due to concrete MVP building stages and valuable customer feedback. Get to know everything about your users and user demand, and succeed in no time.
How to estimate software development time? Find out now!
Frequently Asked Questions
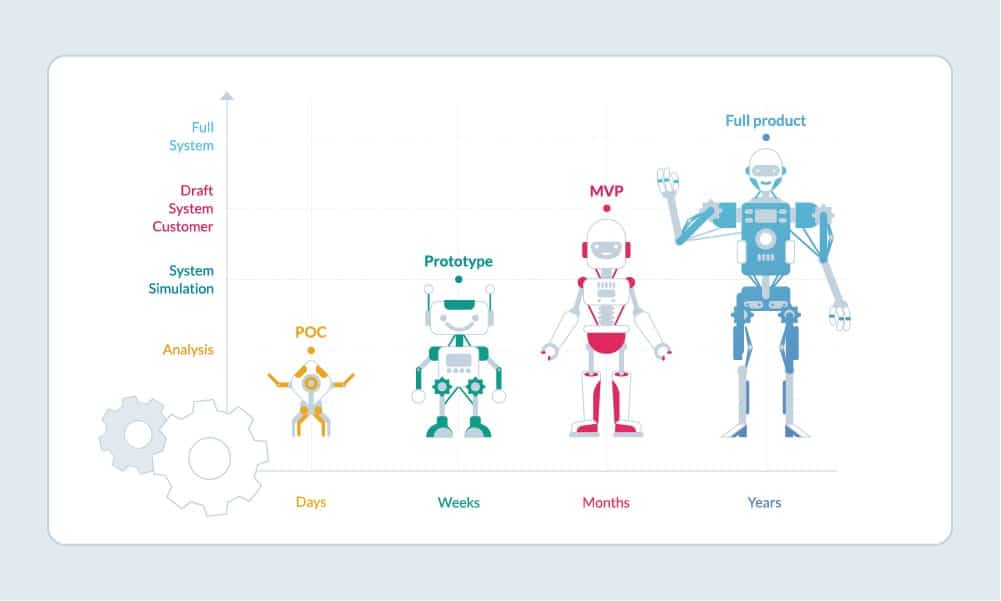
What is the difference between a prototype and a minimum viable product?
How long should it take to build an MVP?
The timeline for building an MVP varies based on project complexity. Typically, it can range from a few weeks to a few months.
Inoxoft's agile approach prioritizes key features for efficient delivery. And even though speed matters, it won't compromise the MVP's effectiveness. For a tailored estimate, let's discuss your project specifics.
What are the reasons for building an MVP?
- User focus approach
- Saves money and time
- Faster time-to-market
- Reduces any development-related risks
- It is better than full product development