Biometric authentication becomes an integral part of personal and commercial security solutions. In 2022, the market for biometric systems was worth $42.9 billion. The experts expect it to grow quickly in the upcoming years, reaching $83 billion by 2027.
Biometric technologies are increasingly seen as commonplace, especially in the banking and fintech sectors. For instance, another research found people are most open to facial recognition in banks (54%), as well as airports (55%), and medical offices (53%). Moreover, 53% of credit card users are ready to switch banks if their current one does not allow biometric authentication in mobile banking.
Biometric security for banking could seem unrivaled given each person's unique biometric characteristics. Biometric banking systems are more secure than those using conventional authentication methods. However, such solutions have their own vulnerabilities cybercriminals can exploit.
This article will review the meaning of biometric authentication, describe the main types of biometric security, and explain how it works. You will learn about the indicators of biometric security, its benefits, key features, and how this technology works in banking.
As experts in banking software development, we will discuss the risks of using biometric authentication and how to tackle security issues. Our NFT marketplace and Trading automation platform development projects will serve as illustrations.
- What Is Biometric Authentication?
- Main Types of Biometric Security
- Biological biometrics
- Morphological biometrics
- Behavioral biometrics
- How Does Biometric Security Work?
- Indicators of Biometric Security
- Facial recognition
- Fingerprint scanning
- Voice recognition
- Iris or retina recognition
- Signature recognition
- Vein recognition
- Gait recognition
- Finger geometry
- How is Biometric Security Used in Banking?
- Bank account opening
- Digital Payments and Money Transfers
- Benefits of Biometric Verification Systems in Digital Banking
- Higher security and reliability
- Simplicity and convenience
- Around-the-clock accessibility
- Saving time
- Making identity fraud impossible
- Cutting costs
- Continuous innovation
- 5 Key Features of Biometric Authentication in Mobile Banking
- Multi-factor authentication
- Transaction data signing
- Mobile security
- APIs
- FFIEC, NIST, and PSD2 compliance
- Risks to Biometric Security for Digital Banking
- Deepfake technology
- Cloning
- Privacy issues
- Ways to Keep Biometrics More Secure
- Multi-factor authentication
- Use of cloud systems
- Tokenization
- Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
- NFT Marketplace for Creators and Collectors
- Trading Automatization Platform
- Maximize Your Mobile Banking App Security with Inoxoft
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a cybersecurity procedure that uses a person’s distinctive biological characteristics (fingerprints, voice, retina, and facial features) to confirm their identity. When a user logs into their account, a biometric authentication system compares their unique biometric features against its database.
This method is more secure and convenient than conventional techniques, like ID cards that can be stolen or passwords that can be guessed. Biometric identification is challenging to trick as it uses distinctive traits to verify identity.
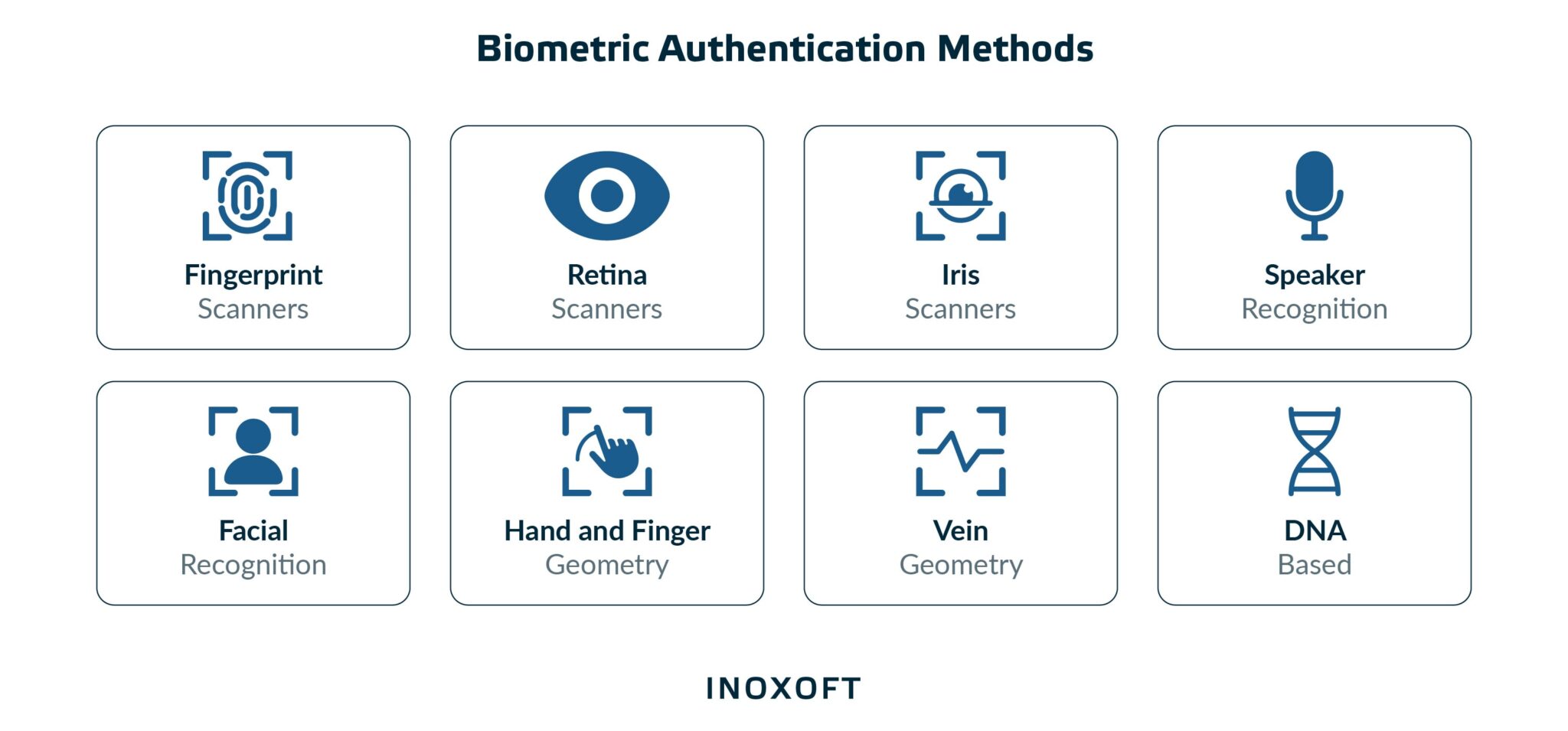
Main Types of Biometric Security
Various forms of biometric technology and data gave birth to different types of biometric security. The kind of hardware or software you are trying to access and the biometric security system guarding it determine how a system validates your identity.
Three different types of biometrics are used:
- Biological
- Morphological
- Behavioral
Biological biometrics
DNA extracted from a blood, saliva, or hair sample is an example of biological material. It is incredibly accurate and frequently used as evidence in criminal cases. However, in most circumstances, the analysis needs to be faster for security control.
Morphological biometrics
Morphological biometrics measure physiological characteristics, studying face, hand, iris, or voice structure. For instance, smartphone biometrics lets you unlock a device with your fingerprint. Also, the airport security system matches your face structure with the one in your passport when you go through a scanner.
Behavioral biometrics
Behavioral biometrics captures distinctive characteristics of what and how you do. For example, everyone types on a keyboard in a specific manner or walks somewhat differently. Also, our handwriting is distinct enough that artificial intelligence can consistently identify people by it. A combination of surfing patterns and specific technology might create a distinctive browsing fingerprint.
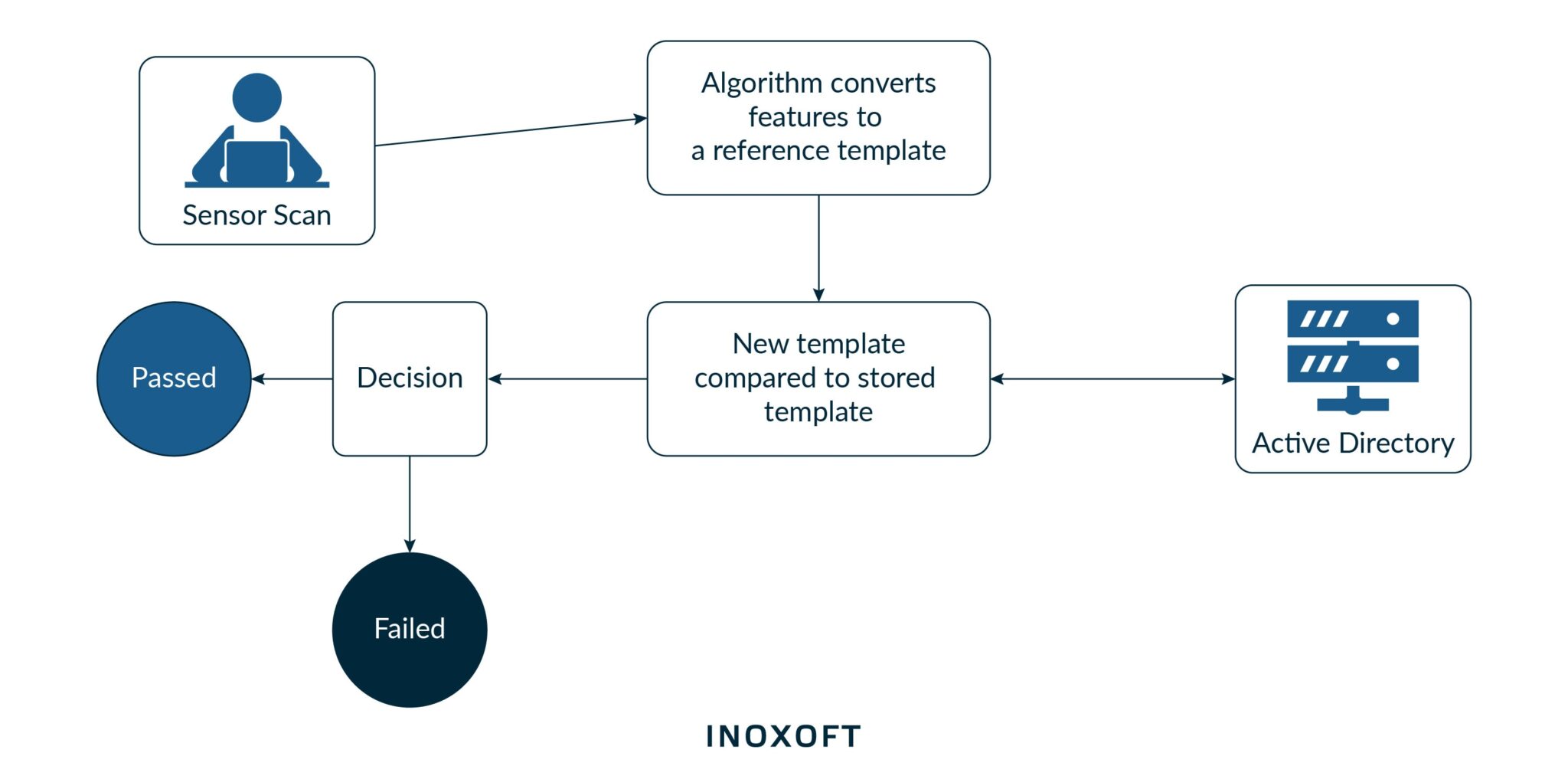
How Does Biometric Security Work?
Scanners for biometric security systems are powered by specialized software that processes the gathered data. Their design varies widely depending on the type of information they get. For instance, it can work with a professional gadget or a tiny scanner in your smartphone.
An activated scanner records biometric information for identity verification. When biometric data has been collected and mapped, it is saved to be matched with upcoming access attempts. This information is frequently encrypted and kept on the device or a remote server.
The associated software automatically digitizes scans and compares them to an existing database. The access is granted if the data samples match. This way, unique biometric data replace other forms of identification, such as passwords.
Indicators of Biometric Security
Before integrating a biometric security system for online banking, you need to choose what information to gather. Some biometric characteristics are easier to measure than others. The primary options to think about are as follows:
Facial recognition
Facial recognition algorithms use convolutional neural networks (CNN) to create and compare face templates or “maps.” The latter capture the appearance and position of key facial features (nose, eyes, mouth). Facial recognition is one of the most often used biometric verification technologies for banking security. This method is quick and simple, as a typical smartphone or laptop camera can capture a face image.
Fingerprint scanning
To build biometric templates, human fingerprint ridge orientation is scanned and digitally recorded. The templates are stored on a dataset. Modern apps employ scanners rather than old-school paper and ink. To provide a fingerprint for contactless identification, a person must place a finger on a platen or hold it before a scanner.
Voice recognition
Voice recognition technology captures frequency, pitch, and accent, which then become unique speech units. Well-known digital assistants employ voice recognition to perform their tasks more quickly and precisely.
Iris or retina recognition
The retina can only be scanned from a close distance, and it takes some time. However, this authentication method is quite accurate. Iris biometric scans are less precise but faster and may be performed from a greater distance. The latest smartphones start to incorporate retina and iris scans for authentication.
Signature recognition
You can use static or dynamic signature recognition. Static recognition involves the algorithm taking a visual image of a handwritten signature and comparing it to the previously recorded one. Dynamic signature recognition assesses the timing, rhythm, and pressure to compare it with the known templates.
Vein recognition
Near-infrared light is used by a finger and hand vein scanner to take pictures of the blood vessel patterns close to the surface of your skin. While a fingerprint duplicate can trick a fingerprint scanner, the blood flow is far more challenging to imitate.
Gait recognition
Every human has a unique gait, a way of walking and running. It differs based on factors including body size, movement speed, stride length and width, angles, and other information captured by a camera. The gait pattern can be used for authentification, diagnostic testing, sports science, medical research, etc.
Finger geometry
Each finger’s form, surface, length, width, and thickness are recorded throughout the biometric scanning process, along with the distance between each finger. The most recent finger geometry systems use three-dimensional imagery for greater accuracy.
Also, a person’s DNA, ear shape, typing style, odor, heartbeat, and other biometric traits can be used for biometric identification.
How is Biometric Security Used in Banking?
Biometric banking technologies help finance organizations improve security and governance. Banking software providers favor biometric data that is simple to gather using a mobile sensor or camera. Thus, facial, voice, and fingerprint identification are the most popular approaches among neobanks. This is how they are used.
Bank account opening
When an account is opened, a bank must confirm customer identity to meet KYC and AML compliance obligations. Biometric identity verification allows banks to digitize the onboarding process. To open a bank account, new clients need to take a photo of their ID and provide their biometric data.
Digital Payments and Money Transfers
Thanks to biometric authentication, we can now use mobile phones to make payments immediately. All it takes is a fingerprint or facial recognition scan. Biometric authentication is also helpful for clients who want to transfer large sums of money. A bank can verify the customer’s identity by asking them to repeat the biometric authentication procedure.
Benefits of Biometric Verification Systems in Digital Banking
Online identity verification now relies heavily on biometric authentication. There are various advantages of biometric system for the banking industry. Let’s focus on the most crucial ones.
Higher security and reliability
Biometric authentication in banking products such as banking apps brings access control to a whole new level. The clients can rest assured that their funds and sensitive information are well protected.
Simplicity and convenience
Biometric security for online banking eliminates the frustration of frequently forgetting strong but convoluted passwords. Unlike remembering passwords or codes, placing our finger on a scanner, taking a picture, or even speaking on the phone does not require any significant effort.
Around-the-clock accessibility
As biometric authentication relies on a person’s unique physical traits, such as fingerprints or facial features, it is accessible 24/7. Without extra authentication tools, biometric scanners enable you to log in from any location at any time.
Saving time
Biometric scans save bank customers’ time and provide a smooth user experience because they are far faster than typing in a password, using a key, or entering a PIN.
Making identity fraud impossible
A unique combination of biometric characteristics can be quite difficult to fake. Biometric security dramatically lowers the danger of phishing, a technique cybercriminals use to wheedle sensitive information.
Cutting costs
The hardware and software for biometric authentication are relatively simple to set up and use. Biometric authentication can offer the highest security in the identity verification process because it doesn’t require users to utilize passwords or usernames.
Continuous innovation
Authentication methods advance along with technology. The most recent step in this direction is behavioral biometrics, which considers person’s habits to determine the legitimacy of banking customers’ operations. These include how they type on the keyboard, the locations they frequently conduct operations from or their purchasing habits.
5 Key Features of Biometric Authentication in Mobile Banking
If you want to implement biometric security in mobile banking, you need to incorporate several critical elements. The following is the fundamental functionality for accurate biometric identification:
- Multi-factor authentication
- Transaction data signing
- Mobile security
- APIs
- FFIEC, NIST, and PSD2 compliance
Multi-factor authentication
Biometric scanning cannot constitute the whole registration process. Banks should provide additional layers of security by asking for a phone number, date of birth, or password check.
Transaction data signing
By issuing a one-time confirmation code, this functionality validates the transaction credentials. It is essential for significant financial transfers, changes to personal information, and other high-risk activities.
Mobile security
Incorporate essential mobile security measures like root detection, sophisticated obfuscation, anti-hooking, and debugging protection. Fighting off possible risks is crucial because a mobile device is a primary platform a neobank uses.
APIs
Build an API if you create a biometric banking security system you provide for third parties. That would simplify its implementation, enabling other companies to introduce biometric scanning quickly.
FFIEC, NIST, and PSD2 compliance
The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) are some of the most important regulations to comply with.
Risks to Biometric Security for Digital Banking
The implementation of biometric technology isn’t risk-free. Even though biometric solutions are more secure than other authentication techniques, the leak of biometric identifiers can have more severe consequences. Let’s look at the most significant concerns.
- Deepfake technology
- Cloning
- Privacy
Deepfake technology
An AI-based system can alter audio, visual, and textual content to depict an event that didn’t actually happen. Deepfakes are particularly dangerous for systems using face recognition.
According to the iProov deepfake report, 77% of cybersecurity experts in financial services are concerned about the fraudulent use of deepfakes. Personal banking and payments are considered the most vulnerable.
Cloning
Fingerprints can be copied from real objects, like a keyboard, or even replicated using a high-resolution image. Researchers have discovered that models created from pictures on Facebook and other social networking sites can fool facial recognition machines. Such face models can be used to breach systems of biometric security for banking based on face recognition authentication.
Privacy issues
Amazon’s Alexa users wondered about the violations of their privacy, wondering whether the virtual assistant is constantly listening to everything they say. The possibility of biometric data being exploited and falling into the wrong hands increases as more gadgets begin to store it. Thus, users should be encouraged to encrypt their traffic via a VPN and employ an anti-tracking tool to disguise their digital footprints.
Learn more about common website security vulnerabilities and how to avoid them in our blog.
Ways to Keep Biometrics More Secure
To reduce the possibility of fraud or data breaches, biometric systems in online banks can have their vulnerabilities fixed. These are the tried-and-true methods to use:
- Multi-factor authentication
- Use of cloud systems
- Tokenization
Multi-factor authentication
Using several biometric security methods or combining biometric scanning with a non-biometric technique are also viable options. For systems that demand the highest level of security, consider combining fingerprints and iris scans, for instance.
Alternatively, you can use two-factor authentication (2FA) to augment biometric security. It will prevent unwanted access even if one authentication mechanism is compromised. One-time security codes delivered via email or SMS are a standard 2FA method.
Use of cloud systems
Although local storage can create a sense of greater control, it is less secure than the cloud. To avoid unwanted access, it is a good idea to work with biometric security suppliers who encrypt their data on the cloud.
Tokenization
Biometric devices are less likely to be compromised if biometric data is concealed within a token or code with no intrinsic meaning or value. The exposure of people’s biometric characteristics is limited because, in the absence of the tokenization system, such tokens are infeasible to reverse.
Read more on mobile banking app security in our blog.
Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
Inoxoft offers services for banking software development to create the best custom banking solutions. We have the best financial software developers in the world to put your creative ideas into practice with the assistance of. You can scale up with Inoxoft’s assistance thanks to its automated processes, enhanced customer service, and security.
We provide banks with functionally robust apps that help cut expenses associated with manual operations, accelerate innovation, and take action on real-time data. With our banking software development services, you will integrate cutting-edge features to support your success with innovative ideas for your custom online banking software.
Let’s look at our success cases delivered by Inoxoft:
NFT Marketplace for Creators and Collectors
The client aimed to develop a web-based NFT platform that makes digital art authentication simple and secure without complex blockchain processes. Inoxoft created the first NFT-based social network developed as a marketplace for artists unfamiliar with blockchain technology. The platform provides tools and functionality for converting digital artworks into NFTs, enabling creators to sell their works directly.
Trading Automatization Platform
A British group of stock traders hired Inoxoft to create an app that would automate the painful process of manual data optimization using algorithms. Inoxoft offered a web application that replaced manual work, prepared sheets automatically with data on optimized exchange rates, and compiled all produced orders for profitable purchases following a defined financial strategy.
Maximize Your Mobile Banking App Security with Inoxoft
The variety of user authentication options that biometric technology provides makes biometric security increasingly popular in the banking and fintech industries. Given its unique identifiers, biometric security for banking may seem invincible. However, multi-factor authentication, tokenization, and storing data in cloud systems can enhance the security of biometric banking systems.
Inoxoft is an international software development company with the highest mobile banking app security standards. We build custom banking software solutions, putting innovative ideas into action to help you scale your business by automating its operations and improving customer service and security.
Contact us to validate your banking software idea and get an estimate for your project.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the trends in biometric authentication?
The latest trends in biometric authentication are related to an increased focus on security and more frequent use of such methods as multimodal and multi-factor authentication, along with privacy regulations.
What is the role of biometric security for banking?
Biometrics helps banks combat insider fraud, better protect customer identities and transaction information, improve user experience, and cut costs.
How does biometric authentication in digital banking work?
Face recognition biometrics captures the image using the device camera (mobile phone, computer, or tablet). A mathematical pattern emerges to link it to identity while accounting for specific features (distance between the eyes, position of the nose, size of the forehead, etc.). Fingerprint biometrics require a scanner, which can be independent or built into a device. To store the fingerprint, fingerprint scanners turn the fingerprint's digital depiction into a digital algorithm.
Are biometric verification systems in banking secure?
Biometric technology is secure enough as it relies on a person’s unique physical traits, such as fingerprints or facial features. It allows banks to fulfill Know Your Client (KYC) requirements. Furthermore, institutions are better guarded against the threats of financial crime and money laundering that frequently accompany fraud. However, using multi-factor authentication is recommended to supplement biometric verification systems.