How to secure database?
- What is cloud infrastructure?
- What is cloud development?
- What is cloud software development?
- What is .net development?
- How does entity framework work?
- Why use entity framework?
- What is entity framework?
- What is ux design process?
- What is ui design skills?
- Why is ux design important?
- What is UI/UX design?
- What is a hybrid app?
- What is native android development?
- What is cross-platform mobile application development?
- What is PostgreSQL used for?
- How to use MongoDB with Nodejs?
- What is Visual Studio Team System (VSTS)?
- What is React Native?
- How to add Firebase to Android app?
- How to estimate a software project?
- How to use firebase database?
Today, every large organization has massive amounts of collected and stored data. This data resides in databases. Thus, databases are the most pursued target by cybercriminals. To avoid cyberattacks, any database should be appropriately secured. How? Let’s find out!
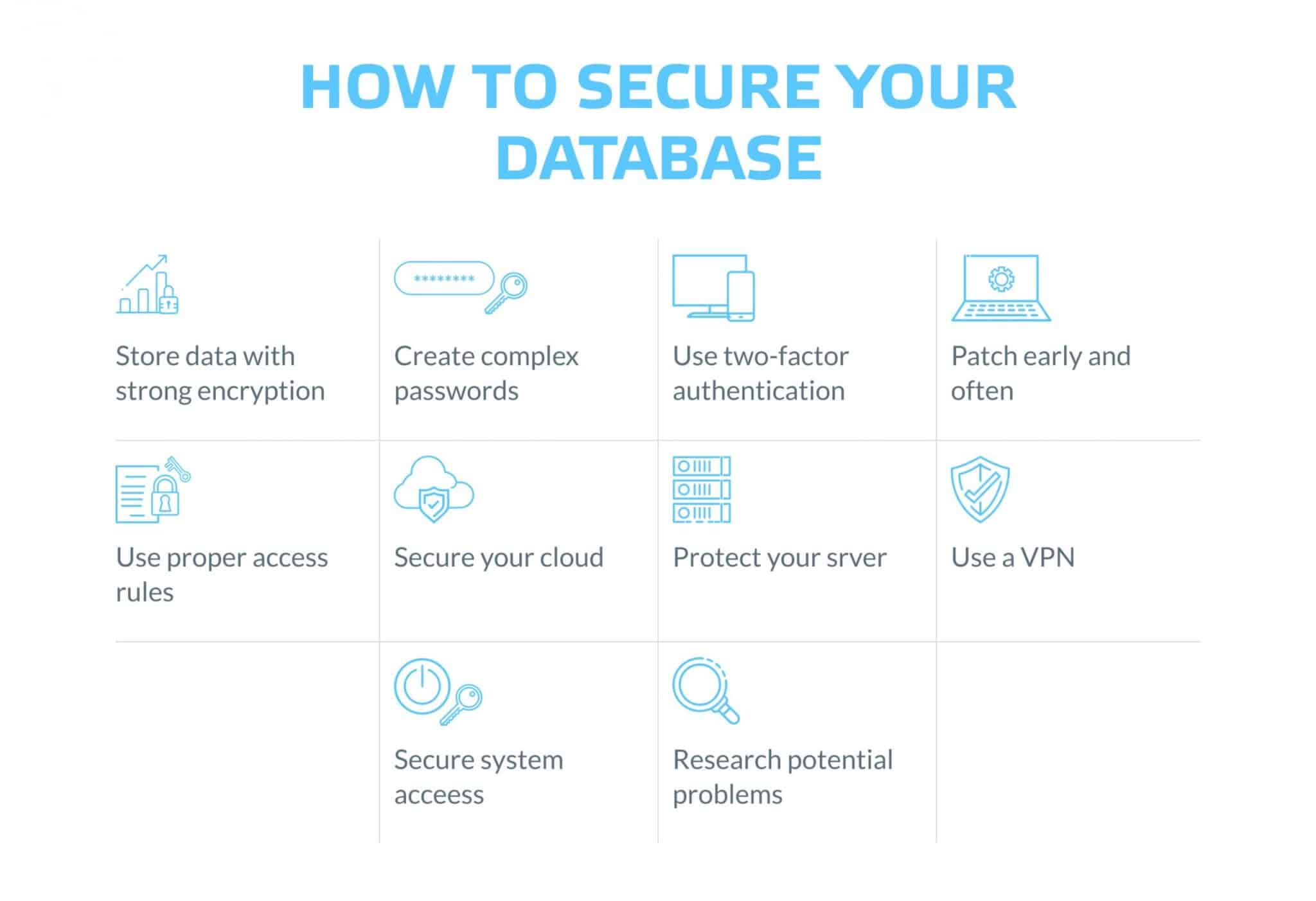
1. Separate database servers and web servers
It is best to keep a database on a separate physical machine, which is differentiated from machines running applications or web servers. In the other words, your database server should be in a secure, locked environment with access controls only for authorized people.
2. Use web application and database firewalls
A firewall is the means to protect your database server from possible security threats. The firewall will deny access to traffic by default except the one, which will go from applications and servers that need to access the data.
Also, you can develop a web application firewall. For example, SQL injection attacks of a web application can be used to extract or erase data from the database. A database firewall won’t cope with this event as an app is an allowed source even if it is bombed with SQL injection attacks.
3. Secure database user access
Only a very small number of people should have access to the database: administrators should have the minimum privileges they need to do the job, smaller organizations should grant permission based on groups or roles. In a larger organization, it is better to use access management software, which makes access an automatic process: authorized users will obtain a temporary password and required privileges to access a database. It also logs everything carried out and prevents administrators from sharing passwords.
In addition, standard account security procedures should be adhered to. For example,
- Strong passwords enforcement
- Stored and encrypted password hashes
- Three or four login attempts are allowed after which accounts should be locked
- Accounts have to be deactivated when workers leave the company
4. Regularly update your operating system and patches
To be protected against all the recent vulnerabilities, it is important to update your operating system and database software with all security patches installed from time to time. Also, all database security controls provided by the database should be enabled unless there is a reason for them to be disabled. This applies especially to those databases connected to a large number of third-party applications and requiring patches.
5. Audit and monitor database activity
- Monitor logins (and attempted logins) to the operating system and database
- Review logs regularly to detect anomalous activity
- Create alerts to be notified about any malicious activity
- Monitor effectively to spot when an account has been compromised, there is suspicious activities or your database is under attack
- Find out whether users tend to share accounts or create them without permission
Database activity monitoring software might give you a hand and provide independent monitoring of native database logging and audit functions. It also helps to monitor administrator activity.
6. Test your database security
After you’ve established your database security infrastructure, you should test it. Hacking or auditing your own database will help you find vulnerabilities if the latter exists. There are third-party services and white hat hackers that you can hire to do the job.
7. Encrypt data and backups
Encrypt your stored data and data-in-transit. Regularly backup your database and ensure that any backups are encrypted and stored separately from the decryption keys.