It’s not a secret that cloud services are really popular nowadays. They are truly convenient to use, they can store loads of data and in general, are a great substitute for traditional ways of storing information. Also, the cloud guarantees you security and reliability, as you know your data is completely safe.
Talking about cloud infrastructure, we can list a lot of things. Software, storage devices, and servers all refer to cloud infrastructure. Also, it is divided into three categories - storage, networking, and computing. Cloud infrastructure management is really helpful for your IT resources and allows you to keep them all in check, monitoring the processes and moving your business forward.
This guide will tell you everything you need to know about cloud infrastructure management in cloud computing and the main features of cloud infrastructure management. Inoxoft has a great experience in cloud computing and software services. If you are interested, this article is for you!
- What Is Cloud Infrastructure Management?
- The Main IT Cloud Infrastructure Components
- How Cloud Infrastructure Management Works?
- The Main Features of Cloud Infrastructure Management
- Automation
- Cost management
- Performance monitoring
- Security
- Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure Management
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Main Cloud Infrastructure Management Tools
- Configuration and provisioning
- Monitoring and visibility
- Allocation of resources
- Using Cloud Infrastructure Management Practices in Software Integration
- Plan ahead
- Tools integration
- Provide security
- Find a partner
- Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
What Is Cloud Infrastructure Management?
The first question is: what is cloud infrastructure management? So, it consists of the processes and tools required to deliver key resources where they are needed. The main benefits of cloud infrastructure management are flexibility, reduced costs, and innovations.
CIMI (or Cloud Infrastructure Management Interface) enables customers to manage a cloud infrastructure easily. Cloud infrastructure comprises hardware and software elements, such as server (compute), networking, storage, and virtualization resources. A user interface also manages all these resources. Cloud services are convenient to external and internal users and are user-friendly for developers and customers equally.
Cloud infrastructure management in software integration helps the company manage its IT resources according to the company’s business needs and priorities. This way, the working processes become automatic, and it saves your time and costs. Old ways of handling data are quite limited, which cannot be said about cloud infrastructure management. Now that cloud infrastructure management and services are tightly integrated, it is a great benefit for those who are looking for reliability and security.
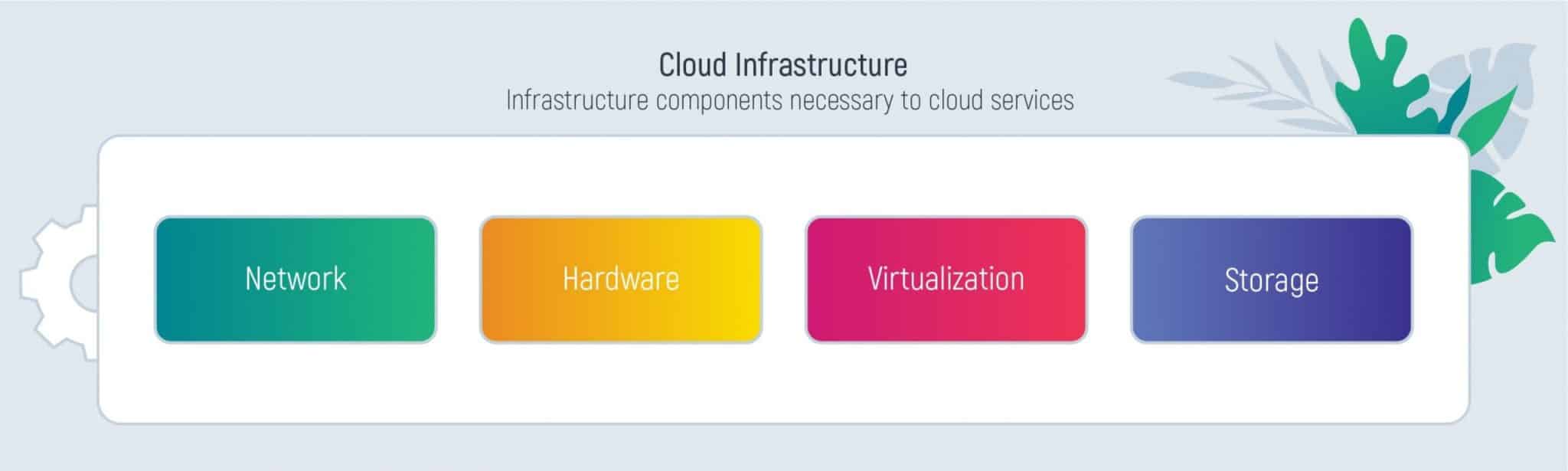
The Main IT Cloud Infrastructure Components
Cloud infrastructure typically consists of several key components that work together to provide a scalable, flexible, and reliable computing environment, which include:
- Network. Cloud resources are typically delivered to users via the internet with the necessary involvement of third-party service providers in constructing and maintaining the networking infrastructure. This infrastructure encompasses physical wiring, switches, load balancers, and routers to ensure the continuous availability of cloud infrastructure for customers.
- Servers. A server, essentially a programmed computer or device, serves as a provider of services to customers or users. In private cloud setups, dedicated servers may be employed for information storage, while public cloud providers utilize a multi-tenant model, where a single server can offer services to multiple customers.
- Storage. Cloud storage services empower organizations to store and manage data on off-site file servers. External cloud storage providers, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Storage, take charge of data management and maintenance, including remote backups. Additionally, cloud infrastructure facilitates the storage of cold data—information not actively in use.
- Virtualization. Virtualization software abstracts computing power and data storage from the underlying hardware, allowing users to interact with their cloud infrastructure through a user-friendly graphical interface. Cloud computing commonly employs virtualization for both computing resources and data storage, streamlining resource utilization for users with increased simplicity and reduced wastage.
How Cloud Infrastructure Management Works?
Efficient management of cloud infrastructure and services consists of many parts that are used in cloud computing. The main parts of it are hardware, storage, virtualization, and network. Even though it is a cloud service, hardware is still important, as it is a physical device. Put simply, it is the basis of every technology.
The principle of virtualization is that software simulates the elements of hardware and creates a virtual environment. All the data is kept in one place, as the storage allows it to be secure. Of course, you have unlimited access to the data, no matter where you are. And the final element is the network, which simply brings all the actions to life and lets the information flow from the cloud to the user’s device.
To sum everything up, the main thing is to maintain a stable connection between the user and the cloud. This is what cloud infrastructure management service is about.
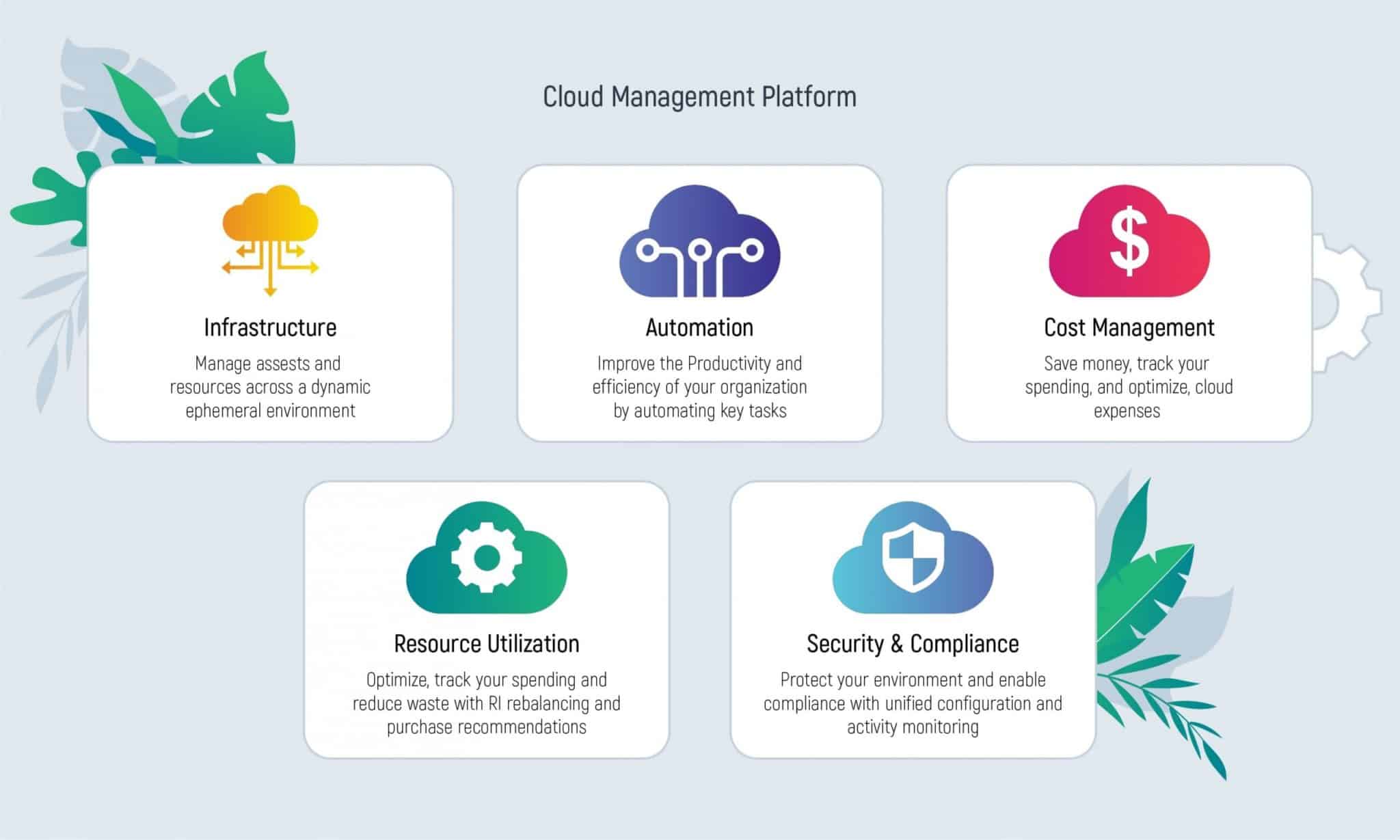
The Main Features of Cloud Infrastructure Management
Cloud infrastructure management practices are really beneficial for your software integration. Many different features are in charge of the successful management of IT resources. Here are some key components of cloud infrastructure management.
Automation
When the processes are automated, it becomes much easier to execute your tasks. It boosts the productivity of your company and saves time for your coworkers.
Cost management
With the help of cloud infrastructure management, you can not only save money but also track your spending. Moreover, it becomes possible to optimize your cloud expenses.
Performance monitoring
You can keep all the processes in check, and it definitely positively influences your work efficiency. On top of that, all the resources are available to everyone, as it is stored in the cloud.
Security
As you have the possibility to monitor all the performance, it gives you safety and effectively protects your environment.
Benefits of Cloud Infrastructure Management
Before you start using cloud infrastructure management best practices, it is important to know its advantages and downsides. Here are some key benefits and hurdles of cloud infrastructure management.
Advantages
We have already mentioned such benefits as reduced costs, security, and compliance. Automated processes and performance monitoring are also really beneficial. A top-notch cloud management platform provides you with comprehensive visualization for your application management. It is great when a cloud infrastructure and management solution supplies you with helpful insights, so you can identify and resolve all your issues.
Disadvantages
Even though cloud infrastructure management is really helpful, it can have its downsides. As the cloud is still an evolving technology, it can cause some vendors to overturn, which can be damaging for a company. If the network connection isn’t stable, it is also an obstacle to proper cloud work. Of course, there are times when access to the cloud is limited
Discover some of the B2B cloud platform advantages!
Main Cloud Infrastructure Management Tools
Cloud infrastructure management tools help engineers managing cloud infrastructure and operations, as well as resolving issues. With their help, you can fully control all the processes and environments. Here are some features of cloud infrastructure management tools.
Configuration and provisioning
The tools help developers set up all the necessary hardware and software resources. They can spin up a new server, install an operating system and distribute storage resources for specific needs.
Monitoring and visibility
Your environment becomes absolutely visible to you if you use cloud infrastructure management tools. They help you check system health and performance, create analytics and provide you with notifications and alerts.
Allocation of resources
Resource allocation gives you the possibility to monitor how users work with cloud resources. It is essential if you want to estimate your budget and see some patterns in cloud infrastructure usage by consumers.
Using Cloud Infrastructure Management Practices in Software Integration
It is already clear that cloud infrastructure management is highly beneficial for software integration. Now it’s high time to consider the best practices of cloud management. Here are some of the key practices Inoxoft recommends.
Plan ahead
Before you start developing your cloud infrastructure, it is highly important to plan everything beforehand. Solving issues post-factum is time-consuming and requires more costs.
Tools integration
If you incorporate existing tools into your cloud environment, it will be much easier for your company to maintain the visibility of the processes.
Provide security
It is your responsibility to monitor if the sensitive information is in safety. Hackers and viruses can also be dangerous to your infrastructure.
Find a partner
If you want to excel in your infrastructure development, it is essential to find a good partner that is experienced and devoted. So finding a responsible partner is half of the deal.
Inoxoft is a company that provides cloud services to customers all around the world. We prioritize our clients’ safety and business needs. Our company will tell you all about the best cloud infrastructure management practices in software integration.
Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
Inoxoft is a worldwide software development company. If you are looking for a dedicated team, automated services and top-notch solutions, our company is what you need.
We provide UI and UX development, quality assurance and testing services, IT system and software integration. Inoxoft uses all the up-to-date technologies, so we will help you implement all the modern features.
Even if you only start to dive into cloud infrastructure, Inoxoft company will support you and fulfill all your requirements. Contact us and get to know everything about cloud services!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the types of cloud infrastructure?
Cloud infrastructure is usually divided into three parts: computing, networking and storage. If you want to know about these parts' functions, scroll up!
Why should you use the cloud infrastructure management?
The main benefits of using cloud infrastructure management are reduced costs, compliance, security, automated processes and performance monitoring. All these things are beneficial for your business.
What are the downsides of using the cloud infrastructure management?
The main disadvantages of using cloud infrastructure management are overturn of vendors, lack of stable network connection and limited access to the cloud.