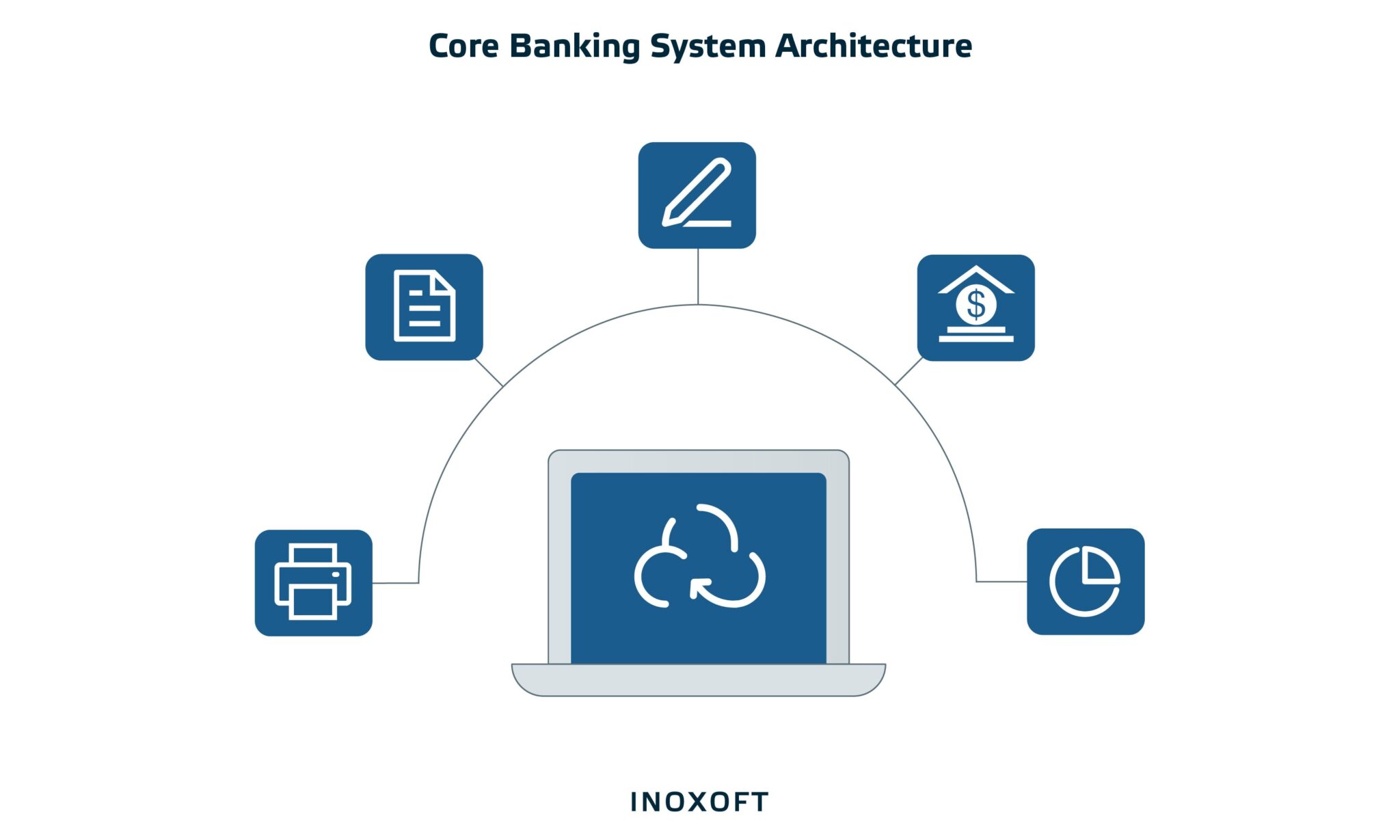
The dated core banking system architecture has been undergoing transformative modernization in recent years. Legacy core banking systems cannot integrate with newer, more effective solutions to supply new business models, goods, and services as swiftly as current, innovative alternatives. Since introducing APIs, cloud services, and digital banking, financial institutions have noticed a significant change in how they deliver their products.
Thanks to recent technological advancements in the banking and financial sectors, a growing number of people access their bank accounts and complete banking transactions online. According to Statista, the share of the population using digital banking services in the United States has increased to 65 percent as of 2022.
The new architecture of core banking system provides financial institutions with the business agility they need. Thus, they can compete with emerging digital challenger banks, also known as neobanks, in an increasingly complex market. Besides, modern technologies and cloud infrastructures lower their operational costs.
This article will help you understand how to implement innovations into existing banking systems or create a modern banking architecture corresponding to all the requirements. We will introduce you to modern core banking systems architecture, essential requirements for new systems, and how to prepare them for implementing innovations.
Finally, we will share the expertise of Inoxoft, an international software development company, in providing innovative banking software development services. Get expert information on creating banking solutions to help you scale up and improve client experience, security, and automated operations.
- What Are the Components and Architecture of the Core Banking System?
- Modern Core Banking Architecture is More Actual than Ever
- 10 Requirements For Modern Core Banking System Architecture
- Cloud readiness
- Open-banking compliance
- API-first
- Self-servicing
- Security
- Flexibility and configurability
- Scalability
- Transparency
- Data digitization
- 24/7 operation with real-time processing
- How to Make Core Banking System Architecture Ready to Implement Innovations
- API platforms for open banking
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Robotic process automation (PRA)
- Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
What Are the Components and Architecture of the Core Banking System?
According to Gartner, the core banking system architecture is a back-end system structure that handles daily banking transactions and posts modifications to accounts and other financial records. Commonly, core banking systems are connected to general ledger systems and reporting tools. They can process:
- Deposits
- Loans
- Credit cards
- Mortgages
- Business loans
Essentially, the core banking system handles credit, loan, and deposit procedures. Creating new accounts, managing loans, calculating interest rates, processing deposits, and withdrawals, and customer relationship management functions are all essential banking services.
There are two types of software architecture of banking system: layered and microservices architecture. Three layers comprise a typical layered architecture of online banking software: the presentation layer (front end), middleware, and backend. The software architecture in banking is often based on microservices. This banking architecture lets you choose when and which functionalities to add or improve.
Modern Core Banking Architecture is More Actual than Ever
The banking industry is disrupted by digital breakthroughs on a seemingly daily basis, decades ahead of legacy financial systems, says Deloitte. Customers now anticipate banks offering the same ground-breaking features and services they often receive from businesses at the forefront of digital innovation.
Traditional banks must still optimize their core banking systems to benefit from cutting-edge technological developments. Otherwise, they fail to meet the market’s increasing expectations, putting themselves at risk and liability. Additionally, the pool of professionals with the technical and institutional knowledge to maintain outdated core systems shrinks. Thus, the operation and maintenance of those legacy systems become increasingly challenging and expensive.
The good news is that more modernization alternatives are now available to banks. Thanks to recent technological advancements and enhanced application management techniques, such options make the work considerably less daunting. Many advantages to modernization include the following:
- Digital competitiveness
- Better talent management
- Improved service
- Reduced risk
- Fewer expenditures
- Increased effectiveness
- Creating value for the company
- Readiness for the future
- Flexibility
- Capturing institutional knowledge
With the core system modernization, banks provide the cutting-edge digital features and capabilities that customers today demand. It opens the way to simplified, standardized, and scalable delivery models that respond swiftly to shifting market needs. These models are far more suitable for the current technology and talent environment.
10 Requirements For Modern Core Banking System Architecture
Establishing a foundation for an effective, open, and inclusive financial system depends on developing products employing modern core banking system architecture or the banking architecture itself. To better understand core banking system modernization, let’s review the requirements for a future-proof banking architecture.
Cloud readiness
The architecture of modern core banking systems is cloud native. Due to their reduced reliance on hardware, cloud-native systems are cheaper to maintain and operate than conventional infrastructure. Agility is another advantage of cloud-native systems since it can significantly shorten the time it takes for new services and products to hit the market.
As traditional infrastructure functions in distinct blocks, with any new update represented by an additional layer, the cloud has significantly shortened the launch period for new goods. Modern core banking system design built on the cloud enables businesses to scale up or down their processes quickly. As a result, banks can save expenses and promptly adapt to changes in client demand and transaction volume without making equipment expenditures.
Open-banking compliance
Banks must expose open APIs to third parties as part of PSD2 regulations, and “open API” enables data sharing between financial and non-financial institutions. The ability to quickly introduce new services to the market and generate additional revenue streams through chances for partnership with other financial and non-financial institutions are notable benefits.
Additionally, by offering better, more individualized support with financial goods and services, core and mobile banking system architecture that is open banking-ready improves client engagement and retention.
API-first
Legacy stack requires custom point-to-point connectors or is incompatible with new suppliers or systems. Therefore, integration with new ones is challenging and takes longer. Modern core banking system architecture is an API-first solution that makes it simple and rapid to add new integrations.
API-first architecture has many ready integrations and a flexible infrastructure to develop new connections with other payment service providers. As a result, financial institutions can create and introduce new services and products considerably more swiftly while maintaining a market-leading position. Moreover, API-first architecture enables the delivery of Banking as a Service (BaaS) solutions to non-fintech and fintech companies, allowing them to integrate financial services without creating stacks from scratch.
Inoxoft has proven expertise in integrating online payment services with CBS. To simplify finance transaction processes, we adapt ‘PayPal-like’ online payment services to your company’s needs. We aim to improve the usability and modernity of your company to add value by providing the ability to accept payments for your products or services. We invite you to integrate premium online payment services to grow your business.
The advantages of using our payment integration services include:
- The transactions are completed quickly and are accessible from any location
- Payment services can be used by phone or custom business
- The transaction policies and certificates ensure the security of every user
- The services adhere to the EMV security standards
Self-servicing
Self-servicing is when clients carry out their routine financial transactions through channels and technologies that support banking. By using any self-service channels, such as online banking or ATMs, they can manage their accounts around the clock without visiting a bank branch.
Self-servicing will become a general requirement that pushes for a more standardized and modernized core banking architecture. Service functions have become much more streamlined and straightforward, and IT personnel are no longer required to remove or add features.
Security
All financial institutions are at greater risk from cyberattacks due to the daily increase in high-profile breaches that steal data and make headlines. Instead of only providing security around specific system components, the modern architecture of banking system should have an enterprise-wide security framework to safeguard the bank and its clients.
The following questions will help to assess the security of the core banking system architecture:
- What protocols do you have for security?
- How can you keep an eye on emerging threats and protect yourself?
- What kind of business continuity and backup services do you provide?
- What credentials does your security staff have, and how much experience do they have?
Flexibility and configurability
Effective financial institutions need a core banking system to tailor it to their requirements without making time-consuming, expensive, or difficult-to-manage changes. Although the system should function out of the box, system administrators should still be able to make necessary adjustments. Switching to a new, more effective environment requires keeping the distinctive workflows specific to the institution.
Scalability
Scalability is a system’s capacity to handle an enormous workload while adding resources. Simply put, it’s how fast an organization can produce more. Scalability comes in two types: vertical and horizontal.
With vertical, the productivity of each system component grows to the point at which the whole system gets scaled. In this case, elements get upgraded to a more powerful version to achieve the desired outcomes more quickly. Horizontal scaling means splitting the system into smaller structural components. Additional servers, processes, and structures must be added to make the entire system scalable.
Financial institutions can use both types of scalability to expand their management capabilities and service offerings. Below are more reasons why banks require scalability.
- Complicated document management
- Large client base
- Wide range of product offerings
- Personnel management
- Multi-processes and task management
Modern technologies, such as artificial intelligence, allow scaling up without compromising the high quality of services and security.
Transparency
An efficient architecture design for banking system should be transparent to facilitate financial reports and audits, as well as to ensure accountability. This tool gives the public a greater understanding of how banks serve their interests and are compliant with the law, ultimately leading to an increase in effectiveness.
Banks need to clarify what they do, how, and why to address the growing responsibilities and significant expansion of balance sheets. It is crucial since their independence has been questioned in many nations. Transparency and accountability are the collateral guarantees of freedom in the context of central banks.
Data digitization
Established technologies, such as sophisticated machine-learning techniques, are available today and can be used to digitize analog data, which is still all too common. Its careful integration with the banking systems and overall architecture should be a focus.
By embracing data digitization, banking institutions can offer better client services. It decreases human error and increases client loyalty. Thanks to the software architecture of online banking system, bank clients may access banks whenever they want. Data digitalization has made extensive cash management simpler and cashless transactions easier. Bank clients can now make transactions anywhere and anytime without storing cash.
24/7 operation with real-time processing
Although almost all banks now offer 24-hour access to their electronic customer channels, there are discrepancies in the information sent there. The banking services range from showing transactions only with a daily update to others displaying account activity on the go. Real-time processing is the goal. Modern banking system architecture should cover real-time processing requirements.
How to Make Core Banking System Architecture Ready to Implement Innovations
The use of cloud infrastructure and emerging technologies will help to comply with the requirements listed above and allow the creation of the architecture for building a core banking system. In more detail, let’s look at cutting-edge technologies that will drive innovations in the modern core banking architecture.
API platforms for open banking
Open banking procedures give non-bank financial companies and other third parties free access to customer banking and additional financial information. It is mainly built on APIs, or application programming interfaces, for open-source software. Open banking, which enables the networking of data and accounts for financial institutions, clients, and outside service providers, has been a significant breakthrough in altering the banking sector.
APIs let reputable external developers create applications and technological interfaces for financial organizations. With this, banks can offer cutting-edge products that improve client experiences. The bank acts as a platform, and other businesses construct applications using the bank’s data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are widely used in various industries, proving they will remain relevant. Al can work in the banking sector for front, middle, and back office tasks, such as:
- Executing credit scoring and improving lending decisions
- Assessing risks
- Identifying and preventing fraud and money laundering
- Creating voice assistants and chatbots
- Streamlining customer authentication and providing users with customized recommendations and offers
Robotic process automation (PRA)
AI-driven virtual assistants are self-learning systems that quickly carry out time-consuming, repetitive jobs. Additionally, thanks to robotic process automation (RPA), banks can generate meaningful customer experiences that are immediate, quick, efficient, and practical, which also automates repetitive operations.
Banks can easily automate tasks like customer onboarding, timely loan processing, account closure, and other functions by combining the power of AI and RPA. They can reduce expenses and increase efficiency by clearly understanding the significant bottlenecks. Through automation, banks are better able to cut back on manual labor and free up their executives’ time for more intricate, strategic responsibilities.
Inoxoft has built a software web application for a trading automation platform. It eliminates manual labor and automatically generates sheets with optimized exchange rate data. In addition, this app compiles all created orders for lucrative purchases following a predetermined financial strategy. Here’s what we’ve achieved, confirming the successful project’s completion:
- Calculating each currency pair continuously from each stock in a queue order
- Order generation is based on calculations using a mathematical formula, order enrollment, and automated order transmission to the broker
- Flawless coordination between the services
- Creating voice assistants and chatbots
- Triple reduction in order generation time
Consider Inoxoft Your Trusted Partner
Thanks to the core system modernization, banks can offer the cutting-edge digital features and capabilities that customers today demand. Additionally, modernization lets you create standardized, scalable, and responsive to changing market demands. A reliable vendor will help you meet today’s requirements for a modern core banking system architecture with enhanced security, automated processes, and superior client experience.
Inoxoft is an international software development company and certified partner that builds market-leading solutions. We provide exceptional banking software development services to help you scale up with improved client experience, security, and automated operations. Under the guidance of the best banking software developers in the world, we create online banking solutions and put creative ideas into practice, including developing a neobank from scratch.
Inoxoft offers bespoke banking software development services to realize the best custom banking solutions, such as:
- Mobile banking architecture
- Loan management and origination systems
- Scaling with innovations
- Customer analytics
- CRM integration
- Security and compliance
- Business process automation
Contact us to discuss your core banking system architecture and get an estimate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a core banking system architecture?
Core banking system architecture serves financial institutions' daily, crucial banking operations, such as payments, cards, and accounts. It is a system in which these items, channels, procedures, and customer management and information tools are united. Core banking systems can be divided into a layered and microservices architecture.
Why do financial institutions require modern core banking architecture?
The goal of a software architecture of digital banking platform is to give financial institutions business agility to compete in a market that is constantly becoming more complex and to lower operating expenses through modern technology and cloud infrastructures.
How to implement digital banking architecture?
Modern digital banking architecture has particular requirements, such as cloud readiness, open-banking compliance, API-first architecture, flexibility, data digitalization, etc. Using cloud infrastructure and cutting-edge technologies, such as API platforms for open banking, AI and ML, and RPA can enable the development of a successful digital banking system.